CCUS: How it Works and Benefits
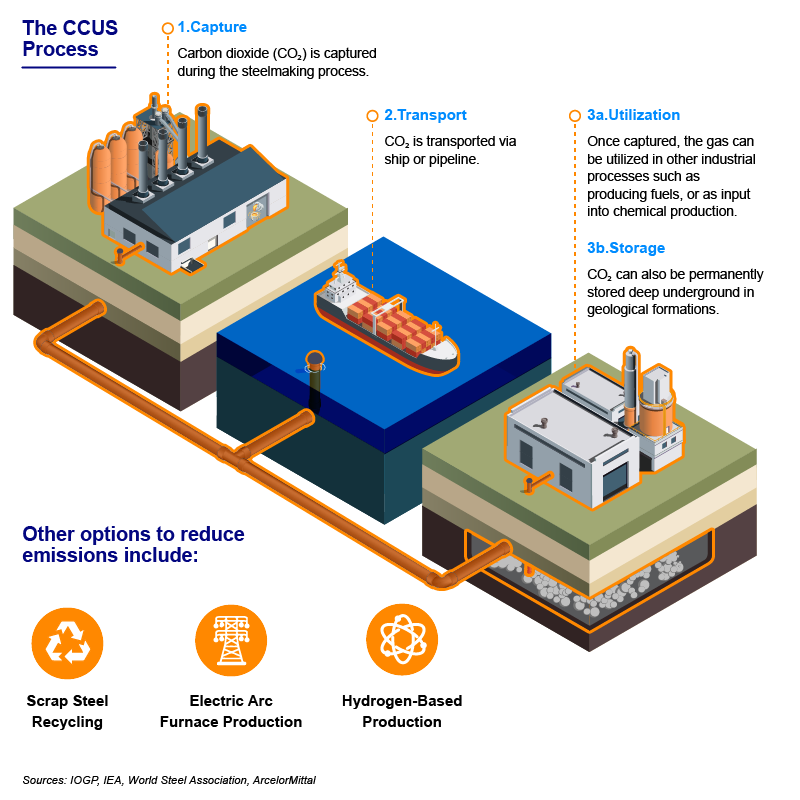
The blast furnace and CCUS technique is the only commercially ready technology capable of decarbonizing the steelmaking industry at the rate and scale required by 2050 to limit global temperature increases to 1.5°C.
Already a proven technology, CCUS is well positioned for large-scale adoption and has the potential to reduce up to 80% of emissions at existing integrated steelmaking facilities. Blast furnace and CCUS is the most cost competitive and commercially viable solution for large-scale decarbonization because it makes use of the over US$1 trillion of newer installed blast furnaces.
Proven technology in hard-to-abate industries
CCUS operates in power generation, refining, petrochemicals, agrichemicals and the steel/iron industry
Blast Furnace + CCUS is commercially viable
Fastest path to large-scale decarbonization
Accelerators to adoption
Large-scale hub and cluster transportation and storage infrastructure will support economies of scale





